The Truth Behind Costco’s Low Prices and What E-commerce Sellers Can Learn from It

Costco, the popular warehouse club, has long been recognized for its ability to offer low prices on a wide range of products. Shoppers flock to its stores in search of deals and discounts on everything from groceries to electronics. Understanding the reasons behind Costco's success can provide valuable insights for e-commerce sellers looking to optimize their pricing strategies.
In the highly competitive world of e-commerce, pricing plays a crucial role in attracting customers and driving sales. By delving into the factors that enable Costco to offer low prices, online sellers can gain valuable knowledge to help them make informed decisions about their own pricing strategies.
This article explores the key elements of Costco's business model that contribute to its ability to provide customers with affordable prices.
Why Can Costco Offer Lower Prices?
There are several reasons why Costco can offer lower prices compared to other retailers.
Here are ten key factors that contribute to Costco's ability to provide cost-effective products and services:
1. Bulk Purchasing Power
One of the primary reasons for Costco's lower prices is its substantial buying power, derived from its bulk purchasing strategy.
- Large quantities: Costco purchases products in large quantities directly from manufacturers and suppliers.
- Negotiating power: Their ability to negotiate lower prices due to the significant volume of products they buy allows them to pass on the savings to their members.
- Cost efficiencies: Bulk purchasing enables Costco to reduce packaging and transportation costs per unit, further lowering the overall price.
2. Limited Product Selection
Costco is known for its limited product selection compared to traditional retailers, but this approach helps them maintain lower prices through the following:
- Streamlined inventory: By offering a narrower range of products, Costco can focus on purchasing large quantities of high-demand items.
- Cost reduction: This strategy minimizes the costs associated with managing extensive inventory and reduces the need for complex storage systems.
- Faster turnover: With fewer choices, Costco can achieve faster inventory turnover, ensuring fresh products and avoiding excess inventory costs.
3. Membership Model
Costco operates on a membership-based business model, which plays a significant role in its ability to offer lower prices.
- Annual fees: Members pay a fee to join Costco, providing the company with a consistent revenue stream and enabling them to sell products at lower margins.
- Exclusive access: The membership model creates a sense of exclusivity, encouraging customer loyalty and repeat visits.
- Cost-sharing: By spreading overhead costs across its membership base, Costco can offset operational expenses and offer products at lower prices.
Costco's membership-based business model offers two tiers: the Gold Star and Gold Star Executive memberships. These options cater to both regular shoppers and business owners, providing exclusive benefits such as access to a wide range of discounted products, bulk purchasing options, and additional perks like higher cashback rewards for executive members.
4. Minimal Marketing Expenses
Unlike many retailers, Costco relies less on traditional advertising and marketing campaigns, allowing them to allocate more resources to providing value to their customers.
- Word-of-mouth reputation: Costco's focus on providing quality products at low prices has generated a strong word-of-mouth reputation among customers.
- Cost savings: By minimizing marketing expenses, Costco avoids passing on advertising costs to its customers, helping to keep prices lower.
- Bulk advertising: When Costco does engage in marketing, it often utilizes cost-effective bulk advertising methods like direct mail or digital campaigns.
Costco's ability to offer lower prices stems from its bulk purchasing power, limited product selection, membership model, efficient store design, and minimal marketing expenses. These factors work together to create a cost-effective retail experience for their members.
5. Direct Relationships with Suppliers
Costco establishes direct relationships with manufacturers and suppliers, eliminating intermediaries and reducing costs.
- Cutting out middlemen: By bypassing wholesalers or distributors, Costco can negotiate better prices directly with suppliers.
- Supplier partnerships: Long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers allow for consistent quality and pricing advantages.
- Collaborative development: Working closely with suppliers, Costco can tailor products to meet customer demands and offer competitive pricing.
What E-commerce Sellers Can Learn from Costco's Business Model
Costco has managed to establish a successful business model that has enabled it to offer low prices to its customers while maintaining profitability.
E-commerce sellers can learn valuable lessons from Costco's approach and apply them to their own online businesses. Here are some key takeaways:
1. Emphasize bulk purchasing and high-volume sales.
Costco thrives on the concept of bulk purchasing.
E-commerce sellers can adopt a similar approach by offering bulk discounts or creating subscription models that encourage customers to purchase more. You can do this by bundling products or giving additional discounts for larger purchases.
By incentivizing volume sales, online sellers can benefit from economies of scale, lower unit costs, and increased customer loyalty.
2. Maintain a limited product selection.
One of Costco's unique features is its limited product selection compared to traditional retailers. Instead of overwhelming customers with an extensive range of choices, Costco focuses on offering a curated selection of high-quality products at competitive prices.
E-commerce sellers can learn from this approach by focusing on a niche market or a specific product category.
By streamlining their product offerings, sellers can simplify the shopping experience for customers, reduce inventory costs, and establish themselves as experts in their chosen niche.
3. Create a membership program.
E-commerce sellers can explore the idea of creating a membership program tailored to their specific business.
Offering exclusive perks, early access to new products, or free shipping can entice customers to join and remain engaged with the brand.
4. Prioritize customer satisfaction and service.
Costco places a strong emphasis on customer satisfaction, offering generous return policies, excellent customer service, and a reputation for standing behind the quality of its products.

By building trust and addressing customer concerns promptly, online sellers can enhance their reputation, encourage positive reviews, and develop long-term customer relationships.
5. Leverage data analytics.
Costco leverages data analytics extensively to optimize its supply chain, manage inventory, and make informed business decisions.
E-commerce sellers can adopt a similar data-driven approach by utilizing analytics tools to gain insights into customer behavior, identify trends, and optimize their operations.
Analyzing data can help sellers identify popular products, tailor marketing campaigns, improve inventory management, and enhance the overall customer experience.
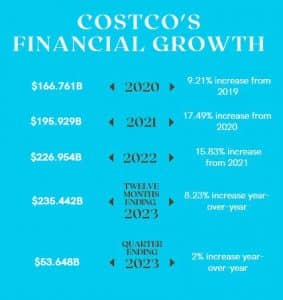
Costco's Financial Performance
Costco has shown impressive financial performance over the years. The company's revenue growth has been consistent and impressive, driven by a combination of factors such as increased membership, store expansion, and strong customer loyalty.
In terms of profits and profit margins, Costco has maintained a healthy financial position. The company's strategy of selling products in bulk and charging membership fees has contributed to its profitability.
When compared to industry competitors, Costco stands out as a leader in the warehouse retail sector. Its financial performance surpasses that of its rivals, including Sam's Club and BJ's Wholesale Club.
Companies with Similar Techniques
Several companies have adopted strategies similar to Costco's successful business model. One notable example is Amazon's Prime membership program. Amazon offers various benefits, including free and fast shipping, access to exclusive deals, and a range of digital services, in exchange for an annual membership fee. This approach has enabled Amazon to build a loyal customer base and drive substantial revenues.
Another company utilizing similar techniques is Walmart's subscription service, Walmart+, which was launched in 2020. Similar to Amazon Prime, Walmart+ offers members benefits such as unlimited free delivery on groceries and other products, fuel discounts, and access to a Scan & Go feature for convenient in-store shopping. Walmart aims to leverage its extensive network of stores and online presence to provide a seamless and value-driven experience for its subscribers. 
By implementing these strategies, Walmart+ seeks to enhance customer loyalty, compete with Amazon's dominance in the e-commerce market, and drive overall sales for the company.
Inspiration Behind Costco's Business Model
Costco was founded in 1983 by James Sinegal and Jeffrey Brotman. The company's business model was inspired by the success of Price Club, a similar warehouse store concept that was gaining popularity at the time. In fact, Price Club merged with Costco in 1993, and the combined company was initially known as PriceCostco before adopting the Costco Wholesale Corporation name in 1997. The original Price Club warehouse in San Diego, California, is still operating as a Costco location.
Costco aimed to offer a unique shopping experience by providing high-quality products at discounted prices through a membership-based model. Over the years, Costco expanded its product range to include a wide variety of goods, from groceries to electronics, while maintaining its commitment to value and customer satisfaction.
James Sinegal's philosophy played a crucial role in shaping Costco's business model. He believed in maintaining a strong company culture, emphasizing employee satisfaction, fair wages, and excellent customer service.
Sinegal's hands-on approach and dedication to ethical business practices fostered a positive work environment and built strong relationships with customers, leading to high customer loyalty and repeat business.
Conclusion
Costco's business model, inspired by Price Club, offers high-quality products at discounted prices through a membership-based approach. James Sinegal's philosophy of employee satisfaction and customer service influenced its success.
Costco's response to changing consumer preferences, including e-commerce and sustainability, highlights its adaptability. This model holds relevance for e-commerce sellers, emphasizing the importance of value, customer relationships, and market adaptability.
Applying Costco's success, businesses can prioritize employee satisfaction, customer-centricity, and innovation to build a strong foundation for growth in a competitive marketplace.