Alibaba vs Amazon: Comparing Two Ecommerce Giants

Alibaba and Amazon are two titans in the ecommerce industry that have transformed how we shop and do business. While both platforms represent a high percentage of global online retail, the way they operate as a business varies in multiple ways.
In this article, we’ll run through the different aspects of both platforms, from their business models, how they generate income, and how Amazon and Alibaba each made their way to the top of the ecommerce industry.
History of Alibaba and Amazon
Alibaba
The history of Alibaba traces back to 1999 when it was created by Jack Ma. It started as an online B2B marketplace to connect Chinese manufacturers to global buyers.
Since then, the company expanded to consumer-focused platforms like Taobao and Tmall, helping it become the leading ecommerce platform in China. Alibaba’s growth continued when they introduced services like Alipay for digital payments and expanded into cloud computing and entertainment.
The innovations made Alibaba a diverse platform influencing the digital world in China and other countries apart from being an ecommerce marketplace. However, it wasn’t until 2014 that the company became known globally. When Alibaba made it on the New York Stock Exchange, it set a record-breaking initial public offering (IPO) of $25 billion.
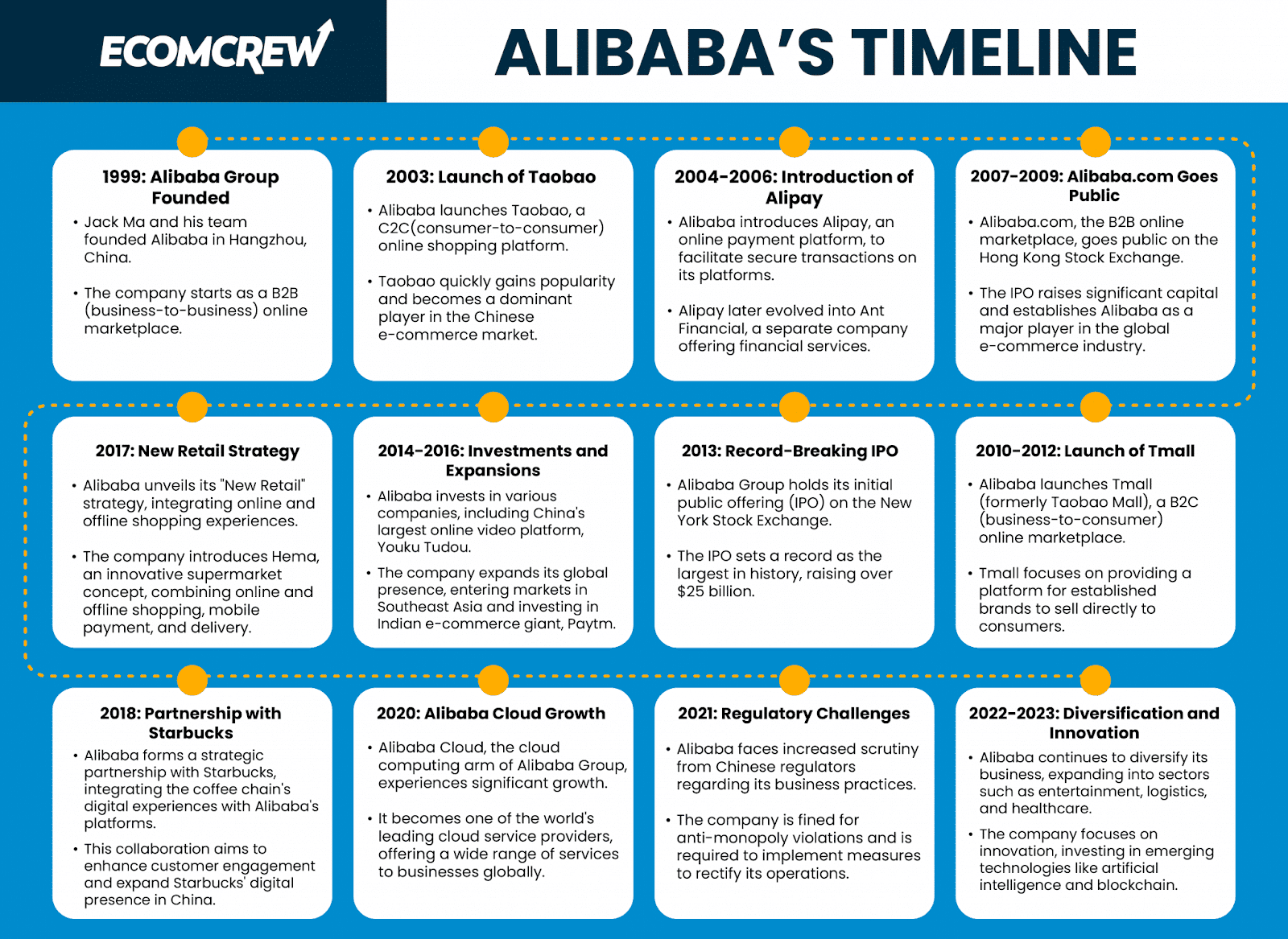
Here’s a look at the full timeline of Alibaba below:
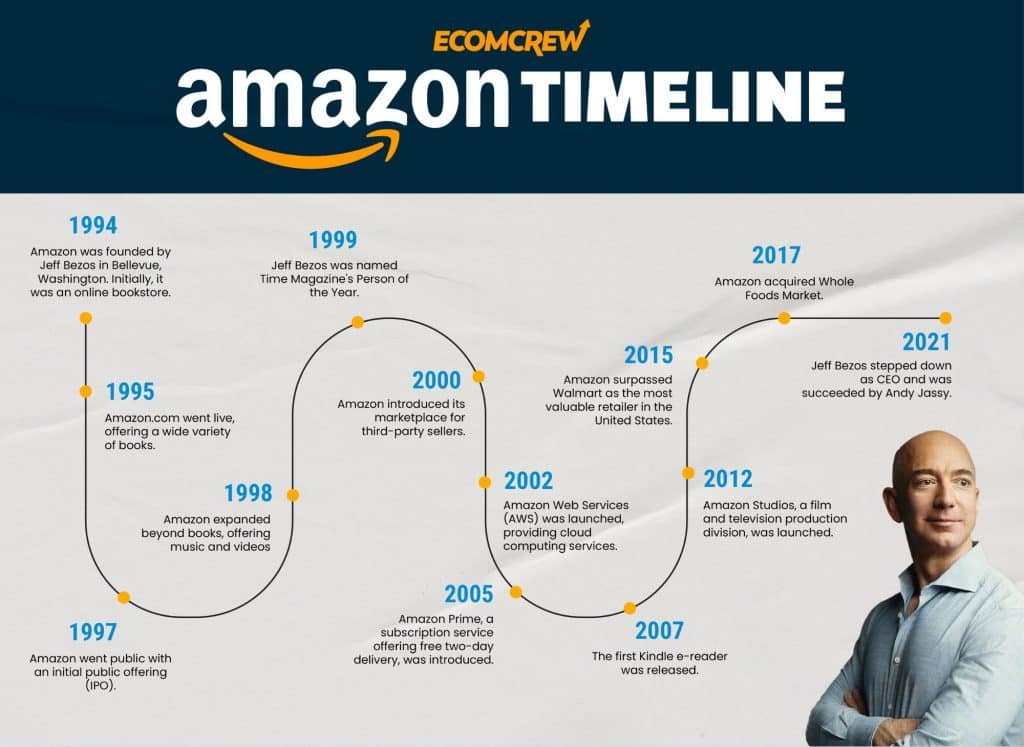
Amazon
Amazon was founded five years earlier than Alibaba by Jeff Bezos.
Operating originally as an online bookstore called “Cadabra” (but was later changed after his lawyer Todd Tarbert said it sounded like “cadaver” on the phone), Amazon’s early success helped the company expand rapidly into all sorts of different categories, including a private label brand, to help it transform into the vast online marketplace we see today.
As for its logo, it’s actually a smiling arrow that starts at the letter A and ends at the letter Z.
This signifies the company's commitment to offering a comprehensive range of goods from A to Z and the arrow's upward trajectory represents progress, growth, and customer satisfaction. The smile is meant to depict a positive and friendly experience for their customers.
Alibaba vs. Amazon: Ecommerce Business Model
At first glance, it may seem like Alibaba and Amazon operate at a similar pace. Both exclusively operate online, make income from commission fees on products, subscriptions to different services, and paid ads.
However, their respective business model as an ecommerce company has distinct features. For starters, Alibaba focuses on B2B transactions while Amazon focuses more on B2C transactions.
What does this mean? For Alibaba, it acts as a middleman between buyers and sellers. This is where you’ll mostly find suppliers and manufacturers who can help you launch a private label brand or dropshipping business.
Alibaba uses several subsidiaries such as AliExpress, Taobao, and Tmall to sell products, unlike Amazon where it's one big marketplace.
| Alibaba ecommerce subsidiary | Year established | Products you'll mostly find | Countries it caters to | Fulfillment services | How the platform makes money |
| AliExpress | 2010 | Products from manufacturers | Global market | 3PL | Commission fees (around 5% to 8%) |
| Taobao | 2003 | Products from manufacturers | China | 3PL | Advertising to increase product visibility |
| Tmall | 2008 | Branded products | Global market | 3PL | Annual fees and commission fees (around 0% to 10%) |
| Lazada Group | 2012 | Mix of generic and branded products | Southeast Asia | 3PL or Fulfilled by Lazada (FBL) | Commission fees (not more than 5%) |
| Trendyol | 2010 | Mix of generic and branded products, and delivery services | Turkey and Europe | Trendyol Express | Commission fees (around 5% to 22%) |
| Daraz | 2015 | Mostly generic products | Southeast Asia | Fulfillment by Daraz (FBD) | 1.75% payment fee, commission fee (around 3% to 16%) |
| Idle Fish | 2014 | Used products | China | 3PL | Advertising to increase product visibility |
| Alibaba Health | 2015 | Pharmaceutical products | China | 3PL | Health products and services |
Amazon focuses more on customer convenience, quick delivery, and a wide selection of products, often leveraging data analytics to personalize recommendations and improve the customer experience. While you will occasionally stumble upon a supplier when scrolling through Amazon, it’s not as common compared to scrolling on Alibaba.
Amazon’s main revenue stream is still its ecommerce marketplace, which made up more than 42% of its income in 2022.
To make revenue outside the ways we mentioned earlier, Amazon also has Amazon Basics and fulfillment services (FBA and MCF) to allow customers to purchase generic products at a lower price and receive them as soon as possible.
Alibaba vs. Amazon: Cloud Computing Services
Alibaba provides a wide range of cloud computing services through Alibaba Cloud, including data storage, power computation, and AI solutions. This segment of Alibaba generates revenue through subscription plans and pay-as-you-go usage fees catered for businesses and developers.
On the other hand, Amazon has Amazon Web Service (AWS), a cloud computing platform that offers scalable and cost-effective cloud computing solutions.
AWS is a widely used cloud platform that provides several on-demand activities such as database storage, host and secure work applications, and content distribution.
Of the two platforms, Amazon has the edge in terms of cloud computing services. AWS has a wider reach than Alibaba Cloud and costs less with the more services you use. However, if you’re a small business, Alibaba Cloud is the better choice since you only pay for what you need.
Alibaba vs. Amazon: Membership Services

To enhance loyalty from customers and encourage frequent purchases, Amazon offers an Amazon Prime membership for a monthly fee (currently $14.99 a month or $139 a year). With this membership, customers are provided with fast and free shipping, access to streaming services (i.e. Amazon Prime Video, Music, etc.), exclusive deals, and unlimited photo storage.
Not to be outdone, Alibaba introduced a premium membership program in 2018 called 88VIP. Members get to enjoy same-day delivery (limited to China), an extra 5% off on products, and coupons for several premium products and services, including Youku (similar to Prime Video), Ele.me (similar to Uber Eats), Fliggy (travel services), and Gaode Taxi (similar to Uber).
Alibaba shoppers can avail of this membership by paying an annual fee of $140. However, if you have more than 1,000 membership points, your annual fee drops to only $13. In both cases, Alibaba does not offer monthly membership options.
Who Generates More Revenue? Amazon or Alibaba?
Between the two e-commerce giants, Amazon generates more annual net sales.
The graphs found that the highest annual revenue of Alibaba (measured only since 2013), was approximately 868.89 billion Yuan, or $126.49 billion, a number eclipsed by Amazon in 2016. Meanwhile, Amazon’s annual net sales revenue peaked at $513.98 billion in 2022.
The good news for both brands is that revenue has continued to grow each year.
Alibaba vs Amazon: Fulfillment Services
This is another aspect where Amazon has a clear edge.
Through the FBA program, Amazon takes all the headaches away from sellers by handling shipping, inventory, and even product returns in exchange for a monthly fee.
With more than 100 fulfillment centers in the United States and over 180 centers spread across the globe, Amazon has continued to find the best way to pick, pack, and ship orders as efficiently as possible by leveraging the use of both humans and advanced robotics. Aside from fulfillment centers, Amazon also has multiple sortation centers that store inventory.

Amazon’s edge mostly lies in its global reach and trust gained from its customers. Outside of China, some people are still skeptical of shopping or sourcing their products from China. Alibaba has introduced somewhat of a similar program to Amazon FBA called Alibaba.com Fulfillment Services (AFS).
It allows you to tap into Alibaba’s trusted network of suppliers immediately and have them handle the negotiation and quality checks as they make their way to you. Overall, this program lets you save on shipping costs since most of the orders are consolidated instead of having them shipped separately.
Alibaba doesn’t charge a monthly fee. Instead, you’re free to choose from verified suppliers and the costs will vary depending on the weight, shipping method, and agreed price with the supplier.
Selling on Each Platform
Market Focus
One big difference between each of the two online marketplaces lies in their target market. Amazon directly caters to consumers, offering both new and used items, whereas Alibaba serves as a middleman connecting buyers and sellers.
However, this doesn’t imply that Alibaba isn’t trying to compete with Amazon. As we mentioned earlier, the company has other seller platforms in AliExpress and Taobao.
When it comes to geographic reach, Amazon has a wider global reach with localized websites for various countries and dominance in the Western markets. Meanwhile, Alibaba primarily focuses on the Chinese market and has a strong presence across Asia.
Fees
This is another significant aspect where you can see notable differences between the two platforms. With both websites, there are some fees and commissions you need to consider.
Seller fees on Amazon
If you want to start selling on Amazon, they offer two seller plans that you can choose from:
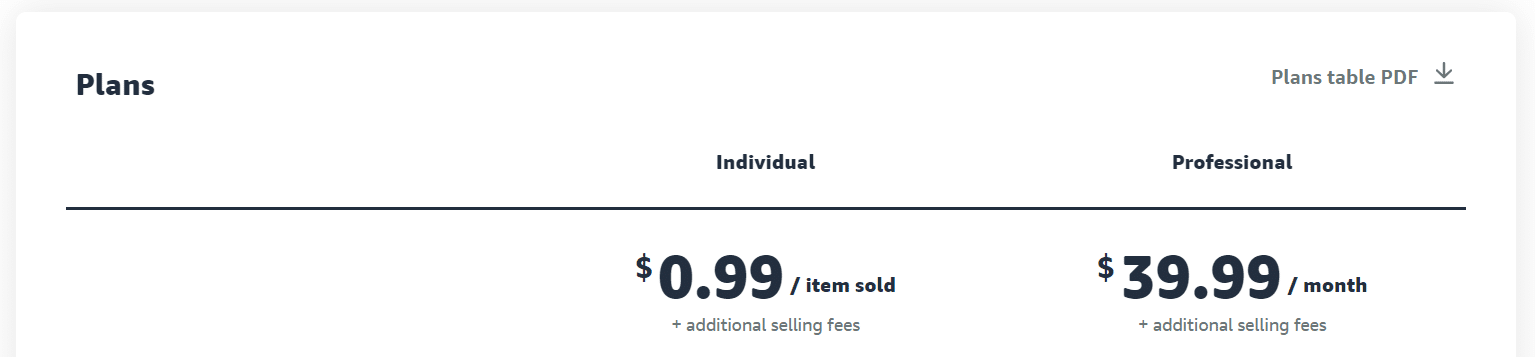
Individual – $0.99/item sold
This plan is ideal for entrepreneurs who sell less than 40 items per month. It may also be best to choose this plan if you don’t have plans to advertise or use some of Amazon’s advanced selling tools and programs.
Professional – $39.99/month
This plan works well for businesses that sell more than 40 items a month and want to qualify for top placement on the product’s detail page.
For each seller plan, you have the option to pay per sale or stick with a flat monthly rate. Of course, in either plan, you have the option to change or cancel anytime. On top of these fees, take note there are other additional fees you have to pay for selling an item, including:
- Closing fees – averaging $1.80
- Referral fees – 8% to 45%
- Shipping fees – $3.99 to $46.50 per order
- Storage fees – $0.69 to $3.40 per cubic foot per month
Recommended reading: Selling on Amazon in Europe: Everything You Need to Know
Seller fees on Alibaba
Alibaba, on the other hand, maintains a relatively loose approach to charging fees, which is evident by its fee-free Taobao platform.
Nonetheless, it’s important to note that selling on the platform isn’t entirely ‘free’. Alibaba gains revenue from sellers who pay to bump their products up the rankings.
Similar to Amazon, Alibaba also offers two types of seller plans that both come with different features that include product posting, receiving and responding to queries, and data reporting.
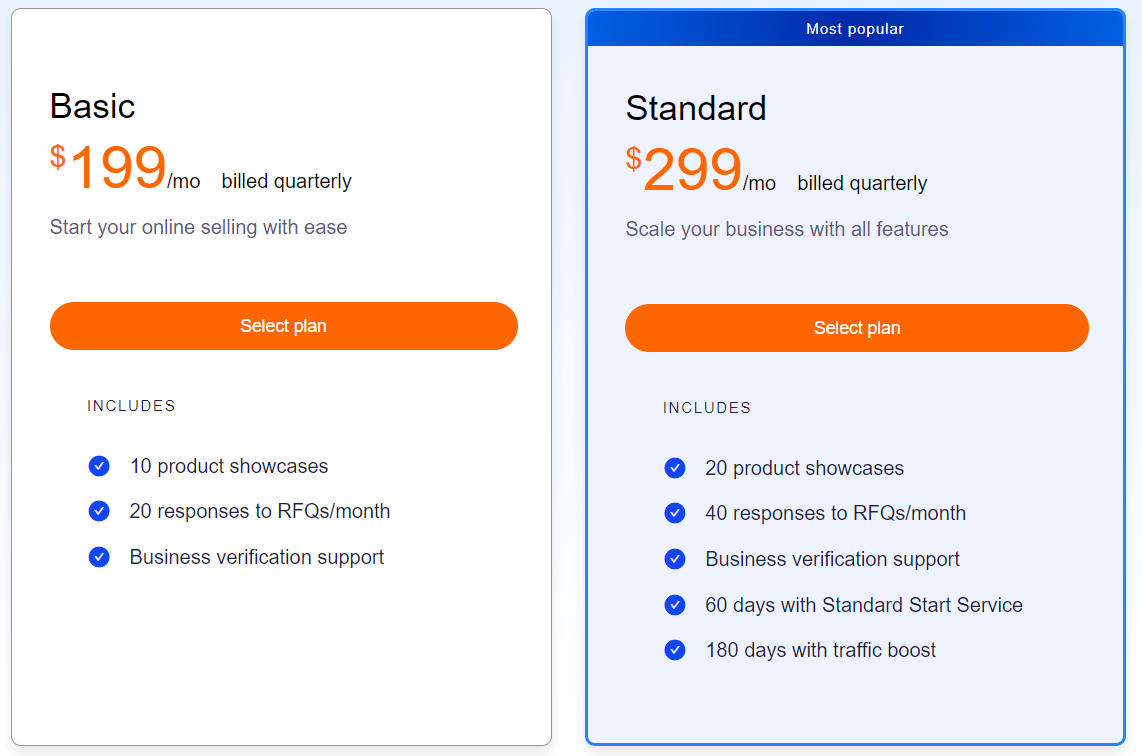
- Basic Plan – $199/month
This plan includes unlimited product listings, 10 product showcases, a customized storefront, 20 responses to RFQ’s (Response to Quotation) per month, and more.
- Premium Plan – $299/month
This plan includes everything in the Basic Plan, plus an additional number of product showcases, responses to RFQ’s, with also full access to Alibaba.com’s Keyword Trends, Smart Marketing automation, and more.
| Fees | Amazon | Alibaba |
| Monthly seller fee | $39.99/ month or $.99 per item sold | $166/ month (if billed annually), $199/ month (if billed quarterly |
| Refund administration fee | Lesser of $5.00 or 20% of referral fee. | 0% |
| Referral fee | Around 8% to 45% of item cost | 0% |
| Listing fee | Free for first 100,000 listings (monthly fee of $0.005 per eligible listing that hasn’t sold in 12 months | Free for first 50 listings (must avail of one of their selling plans afterward) |
Pros and Cons of Each Platform
As two of the top ecommerce marketplaces in the world, both still have their fair share of pros and cons.
Pros of selling on Amazon
- Global customer base
- Convenient for small businesses
- Amazon FBA program
- Amazon FBA program
- Multiple payment gateways for products
Cons of selling on Amazon
- Highly competitive marketplace
- High commission fees per each item sold
- Additional fees to sell on its website.
Pros of selling on Alibaba
- High user traffic with over 20 million active users
- Listing more products will help gain more exposure
- Cheaper alternative to source products
Cons of selling on Alibaba
- Highly competitive marketplace
- Language barriers and cultural differences
- Mostly uses 3PL to fulfill orders
- Longer shipping time
- Mostly uses 3PL to fulfill orders
Final Thoughts
Overall, Alibaba and Amazon have become the global giants in the world of ecommerce by continually finding new ways for both its sellers and customers to have a positive experience.
While both platforms do come with their pros and cons, ultimately it comes down to what your needs are as a business. The competition to get your products noticed is easier on Alibaba than on Amazon, but you do have to factor in shipping costs and the language barrier of selling to a more international market.
Have you tried selling on Alibaba and Amazon? Which platform did you find more success? Let us know in the comments below!